COLOUR GRADING AND COLOUR CORRECTION
- Dec 20, 2017
- 4 min read
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN COLOUR GRADING AND COLOUR CORRECTION?
Colour correction is the primary colour changing for any kind of clip. This makes the image look more natural and gather the correct colours such as the skin colours. It focuses heavily on the amount of light in the colours of the image. Meanwhile, Colour grading focuses on the actual colours in the image, allowing you to alter the colours by balancing the red, greens and blues in the image. Colour correction changes the lighting and colour grading enhances the colours in the image.
COLOUR CORRECTION
Definition: 'Colour correction by using color gels, or filters, is a process used in stage lighting, photography, television, cinematography, and other disciplines, the intention of which is to alter the overall colour of the light; typically the light color is measured on a scale known as color temperature.'
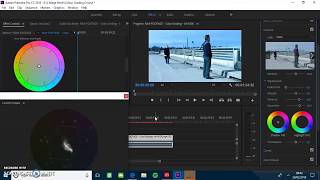
Lumetri scopes is an option that can be found in the windows menu of premiere pro cc. In lumetri scopes, there are multiple preset corrections that you can choose from to cover the image and make it look a certain way. In lumetri scopes there is also an option to get up the scopes for the wavelengths and RGB parade of the image or clip. The wavelengths show the dark and light of colour in the image. Luma is the best setting to see this in as it separates the colours into the black and white ratio. This allows you to easily see which parts of the image or clip have the most light or the most dark. This allows you to change the dynamic range in the image, which is the black and whites from left to right. Curves allow you to change the dynamic range to your preferred look and can change how the shot looks. The "S" curves allow you to create stronger whites or stronger blacks in the image, depending on how the colour looks in your image or clip. There is also an effect that you can add to the clip called "RGB curves" which allows you to edit the colours in them as well which can work alongside the RGB parade. RGB parade shows the red, greens and blues in the image or clip. By choosing this option, you can easily adjust the colours to make them balanced or equal to each other. By doing this, it creates the most natural look in the image and allows you to see the difference by giving a split screen to show the differences. As you can see on the images above, the bottom half is before and the top is afterwards, the top and left looking more realistic in colour tone. There is also something called the fast colour corrector that works alongside the RGB parade and brings up a colour wheel to quickly correct your colours.
The lumetri scopes can also give you the perfect skin tone of any coloured skin. The line between the red and yellow is where the correct colour for skin tone is. The more that the white is on that line, the more correct your skin tone will be. The scope also allows you to see how strong your colours are. If the white goes out of the hexagon, it cannot be shown on TV broadcasts as it makes the images de-saturated or too bright for a TV screen. Going outside of the hexagon is acceptable for internet purposes as this becomes no issue to the screens but will show up differently on every screen. By keeping it in the hexagon, it allows you to get a more constant colour throughout.
When colour correcting, you can change the aperture which will allow you to decide how much light is put into the image or taken out of it. You shouldn't mess with the speed of the clip as it can make the clip jitter. By changing the speed, it interferes with the camera lens sensor which should only be half of the frame speed. By changing the speed it can make the frame speed change and cause a jitter. Blacks and whites cannot be corrected or colour graded as it will add colours to the whites or blacks, making them more of a grey or pink.
COLOUR GRADING
Definition: 'Color grading is the process of altering and enhancing the color of a motion picture, video image, or still image either electronically, photo-chemically or digitally.'
'Black-and-white focuses you on the content and the story, and it really concentrates your attention on what’s in the frame. All too often, color can be a distraction- it’s easier to make color look good, but harder to make color service the story. Black-and-white imagery is much more about the balance between the light and shade in the frame, and I think it can help convey story points a lot better with fewer distractions.' – Roger Deakins
Colour grading is the process of changing the colours in the image and helps to create the different styles in moving image. Colour grading can create a style or mood by changing the exposure, highlights, shadows, whites, blacks and saturation. When bad footage needs to be used, color grading can rescue it. A color grade masks over the technical issues of the footage that helps sell the story. This can often be seen in night footage in documentaries.
The adjustment layer is a quick and easy way to colour grade for all of the footage, adding the same effect over every clip. The adjustment layer can add the same effect to every clip to keep it consistent throughout.
As said earlier, the adjustment layer is able to create an effect over all clips, making it a lot easier to colour grade. It also is able to create the vignette effect and allows you to place it over all of the clips. The adjustment layer is also capable of creating black bars for internet purposes but should not be used for TV broadcast as the TV already has automatic black bars and it would only make your image smaller.
References
"Professional Colour Grading Breakdowns". Jonny Elwyn - Film Editor. N.p., 2017. Web. 9 December 2017.
"Create A Cinematic Look With After Effects Tricks!". YouTube. N.p., 2017. Web. 8 December 2017.
"How To Create A Vignette Effect In Adobe Premiere Pro CS6". YouTube. N.p., 2017. Web. 8 December 2017.
"Color Grading Vs. Color Correction: What's The Difference?". Learning.linkedin.com. N.p., 2017. Web. 9 December 2017.





















Comments